Energy Distribution Measurement of Nonequilibrium Carriers Using a Quantum
Dot
Toshiyuki Kobayashi1,4, Shoei Tsuruta1,3,4, Satoshi Sasaki1, Toshimasa Fujisawa1, Yasuhiro Tokura2, and Tatsushi Akazaki1,4
1Physical Science Laboratory, 2Optical Science Laboratory, 3Tokyo University of Science, 4JST-CREST
A semiconductor quantum dot (QD) confines electrons in a nanometer-scale
region. This results in discrete quantized energy levels of electrons in
a QD. These quantized energy levels can be easily tuned by controlling
the gate voltage, thus enabling us to use a QD as a high-resolution energy
analyzer (or spectrometer) for the electrons near the QD.
We used this feature of QDs to measure the energy distribution of ballistic
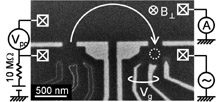
nonequilibrium electrons and holes emitted from a quantum wire (Fig. 1).
Nonequilibrium carriers were emitted by applying a bias voltage (Vpc) to a quantum point contact. The emitted current was again focused by
applying a perpendicular magnetic field (B⊥) and analyzed with a QD (Fig. 2). When the energy of the nonequilibrium
carriers coincides with the quantized energy levels, those carriers can
resonantly tunnel through the QD and can be detected as an electric current.
Therefore, when the quasi-chemical potential of the carriers is aligned
at the energy levels of the QD, the differential conductance of the QD
exhibits a peak and appears as a Coulomb diamonds (Fig. 3).
We found that when the bias energy is small, the energy distribution
does not broaden. However, at a high bias (~1 meV), the distribution broadened
owing to enhanced electron-electron scattering, which causes carrier energy
relaxation [1]. This result is important for future experiments related
to quantum information transfer between quantum bits.
[1] T. Kobayashi, et al., Phys. Stat. Sol. (c) 5 (2008) 162.
 |
|
 |
| Fig. 1. |
Scanning electron micrograph of device and measurement setup. |
|
|
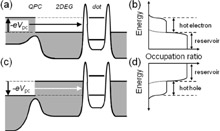
| Fig. 2. |
(a,b) Electron accumulation and (c,d) hole accumulation near quantum dot. |
|
 |
| Fig. 3. |
(a) Coulomb diamond realized by ballistic hot carrier injection. Arrows
indicate peaks caused by hot carriers tunneling through QD levels. (b)
Normal Coulomb diamond by Vsd. |
|
[back] [Top] [Next]


