The spin of a localized electron embedded in a semiconductor quantum dot interacts with the spins of surrounding conduction electrons to form a spin-singlet coherent quantum many-body state. The state is known as the Kondo effect, which changes the state by temperature, electric field, and magnetic field. Since both the localized and conduction electrons play important roles in forming the Kondo state, the Kondo effect should be suppressed if the conduction electrons are spin-polarized. However, any experimental investigation of the Kondo effect with spin-accumulated conduction electrons had been a challenge owing to the difficulty of generating a 100% spin-polarized state. We have succeeded in measuring the continuous modulation of the Kondo effect by accumulating only spin-up electrons near a quantum dot using a spin filter of a quantum wire under a high magnetic field whose spin selectivity is more than 90%.
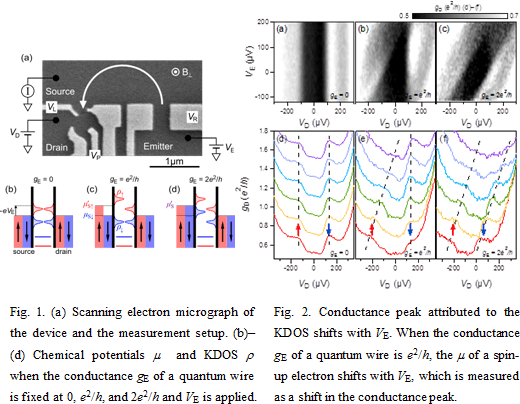
The Kondo effect accompanies the formation of the Kondo density of states (KDOS) at the chemical potential m of a lead, because the conduction electrons at the Fermi energy interact resonantly with the localized electron. Since the KDOS moves with m, changing the m of just the spin-up electrons by injecting only spin-up electrons from a quantum wire to a quantum dot shifts only the spin-up KDOS and modulates the spin-splitting of the KDOS. The position of the KDOS can be measured as a peak in the differential conductance gD of a quantum dot.
[1] T. Kobayashi et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 104 (2010) 036804.